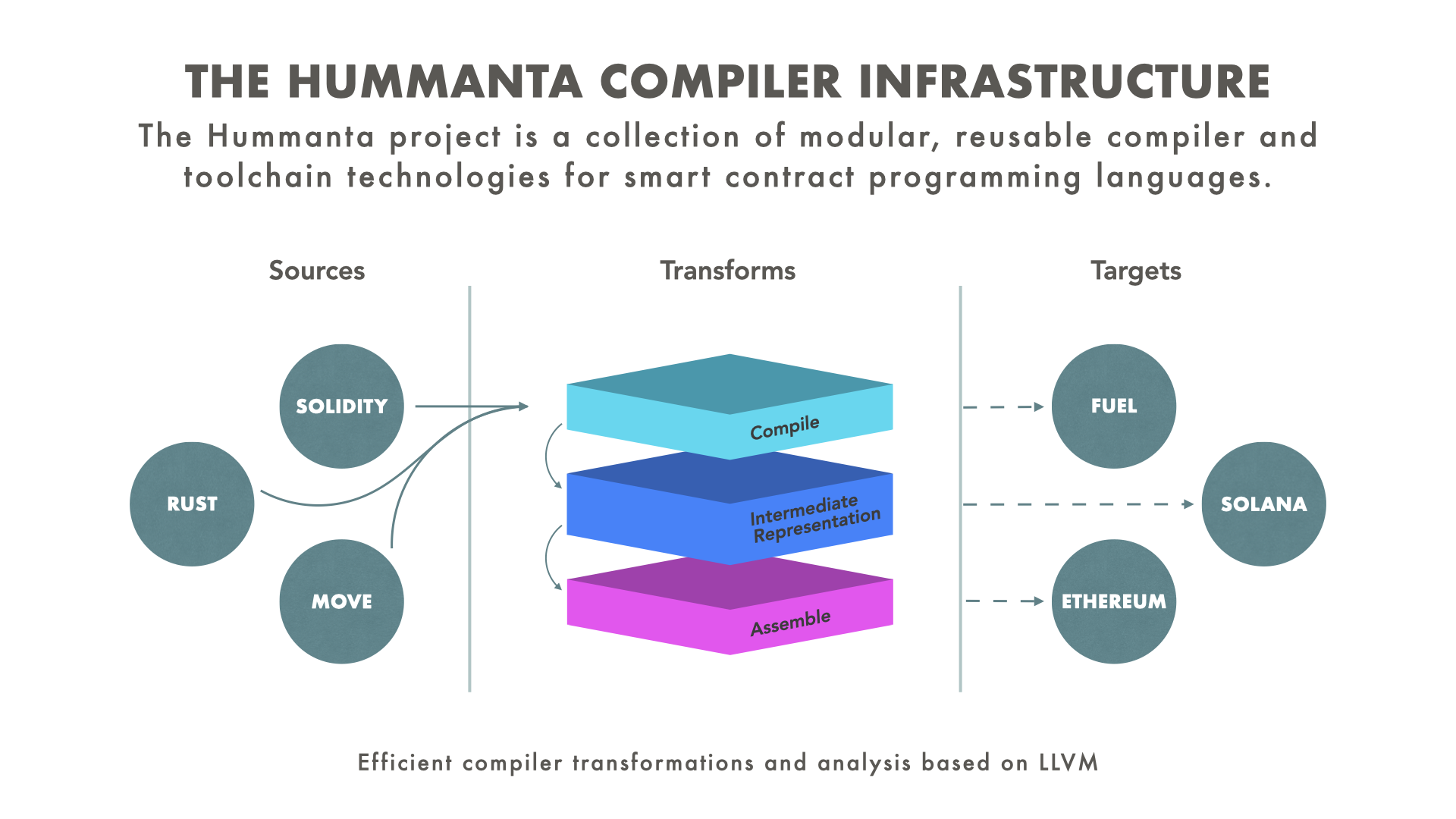
Hummanta is a collection of modular, reusable compiler technologies and a comprehensive framework for rapidly building smart contracts. Designed with flexibility and scalability in mind, Hummanta empowers developers to create efficient, reliable, and secure smart contracts with ease.
The documentation is divided into two main sections:
-
Developers Section: For developers looking to integrate with Hummanta or extend its features by leveraging our modular tools, APIs, and smart contract framework.
-
Users Section: For users who want to learn how to utilize the Hummanta toolchain and framework to streamline their smart contract development workflows.
To join our community and get involved in the development of the Hummanta ecosystem, check out our GitHub repository.
Let’s Get Started!
Getting Started
Welcome to Hummanta! This powerful toolchain is designed specifically for smart contract development. Follow this beginner-friendly guide to get started quickly.
1. Install Hummanta CLI
Prebuilt binaries Windows, Linux and macOS can be downloaded from the Github release page. If there is no distro package available for Hummanta in your preferred manager, you need Rust and cargo to build it.
Install from source:
- Clone the repository with
git clone https://github.com/hummanta/hummanta.git - From the
hummantadirectory, runcargo build --releaseto build the application in release mode. - After a successful compilation, launch the executable with:
target/release/hummanta.
Install with cargo
To get the latest bug fixes and features, you can install the development version from git. However, this is not fully tested. That means you're probably going to have more bugs despite having the latest bug fixes.
cargo install hmt-cli --git https://github.com/hummanta/hummanta
This will download and install the Hummanta CLI in Cargo’s global binary directory (~/.cargo/bin/ by default).
Run hummanta --help for a list of all the available commands. Furthermore, you can run hummanta <command> --help to get help with a specific command.
2. Setup
Install the Required Toolchain
To compile Solidity contracts, install the Solidity toolchain:
hummanta toolchain add solidity
Install the Target Platform
For Ethereum-based smart contracts, add the EVM target:
hummanta target add EVM
3. Start Your First Project
Initializing a new project with Hummanta is straightforward. Run the following command in your project directory:
hummanta init
This command performs two key actions:
- Automatically detects your project type (e.g., Solidity, Rust).
- Generates a
hummanta.tomlconfiguration file.
Now, build your project:
hummanta build
To compile for a specific platform, such as Ethereum or Solana, specify the target:
hummanta build --target=EVM # For Ethereum Virtual Machine
4. Next Steps
Now that you’ve set up Hummanta and built your first project, here are some additional features to explore:
- Manage platforms with
hummanta target - Add language support via
hummanta toolchain
For comprehensive documentation, use:
hummanta --help
Or visit the Hummanta CLI Reference
Happy coding! We can't wait to see the amazing smart contracts you'll build with Hummanta!
Target
In Hummanta, a Target represents the compilation target environment. It determines the format in which the code should be compiled, such as compiling Solidity or Rust code into bytecode compatible with a specific blockchain or virtual machine. The Target mechanism ensures that the code is compiled correctly for various blockchain platforms and virtual machines.
Purpose of Target
The Target mechanism in Hummanta serves several key purposes:
- Specifying Compilation Target: Determines the format in which the code should be compiled, such as compiling Solidity into Solana BPF, Sui MoveVM, or Aptos MoveVM-compatible formats.
- Supporting Multiple Virtual Machines (VMs): Different blockchains use different virtual machines, such as Solana BPF, Sui MoveVM, and Aptos MoveVM. Hummanta provides an adaptation mechanism to ensure proper execution on these VMs.
- Extensibility: Users can add custom Targets and specify corresponding compilation rules, ensuring future support for additional blockchain platforms.
Target Mechanism vs. Rust Target vs. LLVM Target
Hummanta's Target mechanism goes beyond traditional Rust and LLVM targets. It not only defines the target architecture but also includes the overall configuration for the compilation environment.
| Comparison | Hummanta Target | Rust Target | LLVM Target |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Represents a complete compilation target, including compilation format and code transformation tools. | Defines CPU architecture, OS, and ABI for compilation. | Provides a low-level abstraction for generating machine code. |
| Purpose | Adapts to different blockchain environments such as Solana, Sui, and Aptos. | Adapts to different OS and hardware architectures. | Generates IR or machine code for different hardware architectures. |
| Dependency Management | No toolchain management involved. | Requires cross-compilation tools such as rustup target add. | Only includes target architecture information. |
| Extensibility | Easily adds support for new blockchains or virtual machines. | Requires modifying Rust compiler source code. | Requires modifying LLVM source code. |
This comparison highlights that Hummanta's Target is not just a description of a compilation target but a comprehensive system for compiling code for different blockchain environments.
Target Design
Hummanta's Target mechanism is flexible and extensible. While it draws inspiration from Rust's Target system, it provides higher-level dynamic configuration and dependency management capabilities.
1. Configuration-Driven Management
Hummanta manages Targets through hummanta.toml, allowing users to finely configure compilation options, for example:
[target.sui]
compiler = "~/.hummanta/toolchains/sui-move/move-build"
stdlib = "~/.hummanta/toolchains/sui-move/move-stdlib"
output_format = "move-bytecode"
This approach enables users to customize different compilation workflows without manually handling complex low-level implementations.
2. Dynamic Toolchain Management
Hummanta needs to provide specific toolchains for different blockchain ecosystems. The Target mechanism includes a complete dynamic toolchain management solution, including:
hummanta target add <target>: Automatically installs the required compilers, standard libraries, and other components.hummanta target remove <target>: Cleans up related toolchains and dependencies.hummanta target list: Displays available targets and their details.
For example, when a user runs hummanta target add sui, Hummanta automatically downloads and installs the Sui Move compiler while ensuring that the move-stdlib standard library is available.
More details on using target-related commands can be found in the CLI Reference.
3. Automated Compilation Workflow
Hummanta allows users to compile their code using hummanta build, following a structured process:
hummanta build --target=sui
- Parses
hummanta.tomlto determine the target environment. - Loads the appropriate compilation toolchain (which may consist of multiple components).
- Generates bytecode compatible with the target VM.
This process ensures that developers can quickly compile their code without managing underlying tools manually.
Supported Targets
Hummanta currently supports and plans to support the following targets:
- Solana BPF: Compiles Solidity code into Solana-compatible BPF bytecode.
- Sui MoveVM: Compiles Solidity code into Sui-compatible Move bytecode.
- Aptos MoveVM: Compiles Solidity code into Aptos-compatible Move bytecode.
In the future, Hummanta may support additional blockchains and VMs, such as Starknet Cairo, Ethereum zkEVM, and Mina zkApps, enabling developers to deploy contracts seamlessly across multiple chains.
Toolchain
In Hummanta, a Toolchain refers to the set of tools required to compile and transform source code into the target format. It includes compilers, standard libraries, detection tools (Detect), and linkers (Linker), ensuring that the code can be correctly compiled for a specific blockchain platform or virtual machine. A Toolchain is a collection of tools related to a specific language or platform, aimed at ensuring that code compilation, linking, and execution are adapted to the target environment.
Hummanta manages these components through the Toolchain mechanism, providing support for different blockchain or virtual machine platforms, including tools like Detect, Compiler, and Linker.
Features of Toolchain
- Cross-Platform Support: Toolchains provide compilers and tools that support multiple target platforms. For example, the Solidity Toolchain can compile code into bytecode for Solana or Sui environments.
- Flexibility: Users can add, remove, or update toolchains as needed. Hummanta provides a simple command-line interface to manage toolchains and target platforms.
- Automation: During development, the Toolchain automatically manages dependencies, ensuring that the required compilers, standard libraries, and other tools are downloaded and correctly configured.
Components of Toolchain
- Detect: A tool used to detect the project type. It scans project files (e.g.,
.solfiles for Solidity,Cargo.tomlfor Rust) and determines the language and type of the project based on its content. - Compiler: A tool that compiles source code into the target format, such as bytecode or machine code. The compiler adapts to the project type and the target platform (e.g., Solana BPF, Sui MoveVM).
- Linker (Optional): If the generated code requires linking, the linker will combine the compiled modules into a single target file or bytecode.
Toolchain Management
In Hummanta, Toolchain is managed as a set of tool packages. Each toolchain contains a series of tools related to a specific target platform or language. These toolchains can be dynamically installed via the hummanta toolchain add <language> command, so users don't have to manually download or configure the tools.
Toolchain Installation Process
When a user runs hummanta toolchain add <language>, Hummanta automatically downloads the relevant toolchain components from a predefined source (e.g., GitHub Releases or other hosting locations). The process includes:
- Toolchain Lookup: Based on the user's input
<language>, Hummanta checks whether the corresponding toolchain (e.g., Solidity or Rust) is available from the official repository or other mirror sites. - Download Toolchain: Downloads the executable files for the tools (e.g., Detect, Compiler). These files are stored under the
~/.hummanta/toolchains/<language>directory. - Verification and Configuration: Once the download is complete, Hummanta verifies that the toolchain files are executable and correctly configured. If everything is in order, the toolchain becomes ready for use.
Toolchain Management Commands
hummanta toolchain add <language>: Adds the toolchain for the specified language or platform.hummanta toolchain remove <language>: Removes the toolchain for the specified language.hummanta toolchain list: Lists all installed toolchains.
For more details on using toolchain-related commands, refer to the CLI Reference.
Directory Structure
Hummanta stores toolchains under the ~/.hummanta/toolchains/ directory, creating a separate subdirectory for each language or platform, for example:
~/.hummanta/toolchains/
├── solidity/
│ ├── detect # Executable for detecting project type
│ ├── compiler # Compiler executable
│ ├── linker # (Optional) Linker executable
├── rust/
│ ├── detect # Executable for detecting project type
│ ├── compiler # Compiler executable
│ └── linker # (Optional) Linker executable
├── sui-move/
│ ├── detect # Executable for detecting project type
│ ├── move-build # Compiler executable
│ └── move-stdlib # Move standard library
Solidity Language Grammar v0.8.28
Solidity is a statically typed, contract-oriented, high-level language for implementing smart contracts on the Ethereum platform.
Parser Grammar
source-unit
On top level, Solidity allows pragmas, import directives, and definitions of contracts, interfaces, libraries, structs, enums and constants.
import-directive
Import directives import identifiers from different files.
path
Path of a file to be imported.
symbol-aliases
List of aliases for symbols to be imported.
contract-definition
Top-level definition of a contract.
interface-definition
Top-level definition of an interface.
library-definition
Top-level definition of a library.
inheritance-specifier
Inheritance specifier for contracts and interfaces. Can optionally supply base constructor arguments.
contract-body-element
Declarations that can be used in contracts, interfaces and libraries.
Note that interfaces and libraries may not contain constructors, interfaces may not contain state variables and libraries may not contain fallback, receive functions nor non-constant state variables.
call-argument-list
Arguments when calling a function or a similar callable object. The arguments are either given as comma separated list or as map of named arguments.
identifier-path
Qualified name.
modifier-invocation
Call to a modifier. If the modifier takes no arguments, the argument list can be skipped entirely (including opening and closing parentheses).
visibility
Visibility for functions and function types.
parameter-list
A list of parameters, such as function arguments or return values.
constructor-definition
Definition of a constructor. Must always supply an implementation. Note that specifying internal or public visibility is deprecated.
state-mutability
State mutability for function types. The default mutability ‘non-payable’ is assumed if no mutability is specified.
override-specifier
An override specifier used for functions, modifiers or state variables. In cases where there are ambiguous declarations in several base contracts being overridden, a complete list of base contracts has to be given.
function-definition
The definition of contract, library, interface or free functions. Depending on the context in which the function is defined, further restrictions may apply, e.g. functions in interfaces have to be unimplemented, i.e. may not contain a body block.
modifier-definition
The definition of a modifier. Note that within the body block of a modifier, the underscore cannot be used as identifier, but is used as placeholder statement for the body of a function to which the modifier is applied.
fallback-function-definition
Definition of the special fallback function.
receive-function-definition
Definition of the special receive function.
struct-definition
Definition of a struct. Can occur at top-level within a source unit or within a contract, library or interface.
struct-member
The declaration of a named struct member.
enum-definition
Definition of an enum. Can occur at top-level within a source unit or within a contract, library or interface.
user-defined-value-type-definition
Definition of a user defined value type. Can occur at top-level within a source unit or within a contract, library or interface.
state-variable-declaration
The declaration of a state variable.
constant-variable-declaration
The declaration of a constant variable.
event-parameter
Parameter of an event.
event-definition
Definition of an event. Can occur in contracts, libraries or interfaces.
error-parameter
Parameter of an error.
error-definition
Definition of an error.
user-definable-operator
Operators that users are allowed to implement for some types with using for.
using-directive
Using directive to attach library functions and free functions to types. Can occur within contracts and libraries and at the file level.
using-aliases
type-name
A type name can be an elementary type, a function type, a mapping type, a user-defined type (e.g. a contract or struct) or an array type.
elementary-type-name
function-type-name
variable-declaration
The declaration of a single variable.
data-location
expression
Complex expression. Can be an index access, an index range access, a member access, a function call (with optional function call options), a type conversion, an unary or binary expression, a comparison or assignment, a ternary expression, a new-expression (i.e. a contract creation or the allocation of a dynamic memory array), a tuple, an inline array or a primary expression (i.e. an identifier, literal or type name).
tuple-expression
inline-array-expression
An inline array expression denotes a statically sized array of the common type of the contained expressions.
identifier
Besides regular non-keyword Identifiers, some keywords like ‘from’ and ‘error’ can also be used as identifiers.
literal
literal-with-sub-denomination
boolean-literal
string-literal
A full string literal consists of either one or several consecutive quoted strings.
hex-string-literal
A full hex string literal that consists of either one or several consecutive hex strings.
unicode-string-literal
A full unicode string literal that consists of either one or several consecutive unicode strings.
number-literal
Number literals can be decimal or hexadecimal numbers with an optional unit.
block
A curly-braced block of statements. Opens its own scope.
unchecked-block
statement
if-statement
If statement with optional else part.
for-statement
For statement with optional init, condition and post-loop part.
while-statement
do-while-statement
continue-statement
A continue statement. Only allowed inside for, while or do-while loops.
break-statement
A break statement. Only allowed inside for, while or do-while loops.
try-statement
A try statement. The contained expression needs to be an external function call or a contract creation.
catch-clause
The catch clause of a try statement.
return-statement
emit-statement
An emit statement. The contained expression needs to refer to an event.
revert-statement
A revert statement. The contained expression needs to refer to an error.
assembly-statement
An inline assembly block. The contents of an inline assembly block use a separate scanner/lexer, i.e. the set of keywords and allowed identifiers is different inside an inline assembly block.
assembly-flags
Assembly flags. Comma-separated list of double-quoted strings as flags.
variable-declaration-tuple
A tuple of variable names to be used in variable declarations. May contain empty fields.
variable-declaration-statement
A variable declaration statement. A single variable may be declared without initial value, whereas a tuple of variables can only be declared with initial value.
expression-statement
mapping-type
mapping-key-type
Only elementary types or user defined types are viable as mapping keys.
yul-statement
A Yul statement within an inline assembly block. continue and break statements are only valid within for loops. leave statements are only valid within function bodies.
yul-block
yul-variable-declaration
The declaration of one or more Yul variables with optional initial value. If multiple variables are declared, only a function call is a valid initial value.
yul-assignment
Any expression can be assigned to a single Yul variable, whereas multi-assignments require a function call on the right-hand side.
yul-if-statement
yul-for-statement
yul-switch-statement
A Yul switch statement can consist of only a default-case (deprecated) or one or more non-default cases optionally followed by a default-case.
yul-function-definition
yul-path
While only identifiers without dots can be declared within inline assembly, paths containing dots can refer to declarations outside the inline assembly block.
yul-function-call
A call to a function with return values can only occur as right-hand side of an assignment or a variable declaration.
yul-boolean
yul-literal
yul-expression
Lexer Grammar
fixed-bytes
Bytes types of fixed length.
sub-denomination
Unit denomination for numbers.
signed-integer-type
Sized signed integer types. int is an alias of int256.
unsigned-integer-type
Sized unsigned integer types. uint is an alias of uint256.
non-empty-string-literal
A non-empty quoted string literal restricted to printable characters.
empty-string-literal
An empty string literal
single-quoted-printable
Any printable character except single quote or back slash.
double-quoted-printable
Any printable character except double quote or back slash.
escape-sequence
Escape sequence. Apart from common single character escape sequences, line breaks can be escaped as well as four hex digit unicode escapes \uXXXX and two digit hex escape sequences \xXX are allowed.
unicode-string-literal
A single quoted string literal allowing arbitrary unicode characters.
hex-string
Hex strings need to consist of an even number of hex digits that may be grouped using underscores.
hex-number
Hex numbers consist of a prefix and an arbitrary number of hex digits that may be delimited by underscores.
decimal-number
A decimal number literal consists of decimal digits that may be delimited by underscores and an optional positive or negative exponent. If the digits contain a decimal point, the literal has fixed point type.
identifier
An identifier in solidity has to start with a letter, a dollar-sign or an underscore and may additionally contain numbers after the first symbol.
yul-evm-builtin
Builtin functions in the EVM Yul dialect.
yul-identifier
Yul identifiers consist of letters, dollar signs, underscores and numbers, but may not start with a number. In inline assembly there cannot be dots in user-defined identifiers. Instead see yulPath for expressions consisting of identifiers with dots.
yul-hex-number
Hex literals in Yul consist of a prefix and one or more hexadecimal digits.
yul-decimal-number
Decimal literals in Yul may be zero or any sequence of decimal digits without leading zeroes.
yul-string-literal
String literals in Yul consist of one or more double-quoted or single-quoted strings that may contain escape sequences and printable characters except unescaped line breaks or unescaped double-quotes or single-quotes, respectively.
pragma-token
Pragma token. Can contain any kind of symbol except a semicolon. Note that currently the solidity parser only allows a subset of this.
References
Sway Language Grammar v0.66.5
Sway is a domain-specific programming language for implementing smart contracts on blockchain platforms, most notably for the Fuel Virtual Machine (Fuel VM).
Parser Grammar
module
On top level, Sway allows module kind and definitions of submodule, storage, contracts, traits, libraries, structs, enums and constants. (AST: Module)
submodule
The mod keyword registers a submodule, making its items (such as functions and structs) accessible from the parent library. If used at the top level it will refer to a file in the src folder and in other cases in a folder named after the library in which it is defined. (AST: Submodule)
use
Provides several utility types and methods we can use in our contract. (AST: ItemUse)
use-tree
Path of a types or methods to be imported. (AST: UseTree)
struct
Definition of a struct. Can occur at top-level within a source unit or within a contract, library or interface. (AST: ItemStruct)
type-field
Definition of TypeField. (AST: TypeField)
type-name
Definition of TypeName. (AST: Ty)
enum
Definition of an enum. Can occur at top-level within a source unit or within a contract, library or interface. (AST: ItemEnum)
traits
Definition of traits. Can be used for abi and trait.(AST: Traits)
trait-item
Define an item of an trait. (AST: ItemTraitItem).
abi
ABI stands for Application Binary Interface.(AST: ItemAbi, doc: The ABI Declaration).
const
Define constant items. (AST: ItemConst)
configurable
Configurable constants are special constants that behave like regular constants in the sense that they cannot change during program execution, but they can be configured after the Sway program has been built. (AST: ItemConfigurable, doc: Configurable Constants)
type-alias
Definition of type-alias. To declare a type alias to give an existing type another name. (AST: ItemTypeAlias)
fn
Functions in Sway are declared with the fn keyword. (AST: ItemFn, doc: Functions)
fn-signature
fn-signature declares signature for function. (AST: FnSignature, doc: Functions)
generic-params
Generic types are a way to refer to types in general, meaning without specifying a single type. (AST: GenericParams, doc: Generic Types).
where-clause
Where clause can be used to specify the required traits for the generic argument. (AST: WhereClause, doc: Trait Constraints).
code-block-contents
A CodeBlockContents represents the body of a code block, which contains a sequence of statements and expressions. (AST: CodeBlockContents, doc: Functions).
fn-arg
A fn-arg represents function arguments. (AST: FnArg, doc: Functions).
pattern
A pattern is a construct used to match and destructure data. (AST: Pattern, doc: match expressions).
trait
A trait opts a type into a certain type of behavior or functionality that can be shared among types. This allows for easy reuse of code and generic programming. (AST: ItemTrait, doc: Declaring a Trait).
impl
Implement inherent or trait functionality. (AST: ItemImpl, doc: Implementing a Trait)
storage
In smart contract development, persistent storage (storage) is used to store values that persist after the contract exits, unlike regular memory values that disappear. (AST: ItemStorage, doc: Declaring storage)
storage-entry
Define storage entry. (AST: StorageEntry, doc: Declaring storage)
expr
Define types of expressions. (AST: Expr, doc: If Expressions)
path-expr
Define of path expressions, such as module or function access. (AST: PathExpr)
qualified-path-root
It is a part of path-expr or path-type.
Define a type with an optional trait alias, allowing the expression of a qualified path that includes a type and optionally a trait it is associated with. (AST: QualifiedPathRoot)
path-expr-segment
It is a part of path-expr or method-call expr.
Define a segment of a path expression, consisting of a name (identifier) and optionally associated generic arguments with a :: separator. (AST: PathExprSegment).
path-type
Define a type path, consisting of an optional qualified root, a prefix, and a series of suffixes, each potentially followed by generic arguments, to express complex type references. (AST: PathType).
generic-args
It is a part of path-expr or path-type.
Define the generic type parameters enclosed in angle brackets (<>), where the parameters are a punctuated list of types separated by commas. (AST: GenericArgs).
Sui Move Language Grammar (mainnet-v1.43.1)
A next generation language for secure asset programming. Its primary use case is in blockchain environments, where Move programs are used to construct state changes. Move allows developers to write programs that flexibly manage and transfer assets, while providing the security and protections against attacks on those assets.
Parser Grammar
module
Modules are the core program unit that define types along with functions that operate on these types. (AST: ModuleDefinition, Doc: Modules)
enum-definition
An enum is a user-defined data structure containing one or more variants. Each variant can optionally contain typed fields. The number, and types of these fields can differ for each variant in the enumeration. Fields in enums can store any non-reference, non-tuple type, including other structs or enums. (AST: EnumDefinition, Doc: Enumerations)
type-parameters
This type is used in multiple places. To avoid redundant definitions, a shared virtual type is created to simplify imports.
type-parameter
Both functions and structs can take a list of type parameters in their signatures, enclosed by a pair of angle brackets <...>. (AST: DatatypeTypeParameter, Doc: Declaring Type Parameters)
abilities
This type is used in multiple places. To avoid redundant definitions, a shared virtual type is created to simplify imports.
ability
Abilities are a typing feature in Move that control what actions are permissible for values of a given type. (AST: Ability, Doc: Abilities)
doc-comment
Documentation comments are special comments that are used to generate documentation for your code. They are similar to block comments but start with three slashes /// and are placed before the definition of the item they document. (AST: DocComment, Doc: Doc comment)
Hummanta CLI Reference
Overview
Hummanta is a tool for compiling multiple languages, supporting the build and compilation of projects such as Solidity and Rust. The toolchain provides a flexible command-line interface, allowing users to easily manage and compile code for different target platforms. The following commands are available for building, managing, and configuring the workspace:
Usage: hummanta <COMMAND>
Commands:
build Builds the entire workspace
init Initializes the workspace
target View and manage compilation targets
toolchain Manage compilation toolchains
help Print this message or the help of the given subcommand(s)
Options:
-h, --help Print help
Init
Automatically detects the type of the current project (e.g., Solidity or Rust) and generates a hummanta.toml configuration file.
hummanta init
Build
Builds the entire project and compiles the source code files.
hummanta build --target=<target>
Target
View and manage compilation targets.
hummanta target add <target>
hummanta target remove <target>
hummanta target show <target>
hummanta target list
add: Adds a new target configuration.remove: Removes the specified target configuration.show: Displays the details of the specified target.list: Lists all targets.
For more information about the target, see the core concept Target.
Toolchain
View and manage different toolchains used for the compilation process.
hummanta toolchain add <language>
hummanta toolchain remove <language>
hummanta toolchain show <language>
hummanta toolchain list
add: Installs the specified language's toolchain.remove: Removes the toolchain for the specified language.show: Displays the details of the the specified language's toolchain.list: Lists all toolchains.
For more information about the toolchain, see the core concept Toolchain.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How do I switch the target platform?
You can specify the target platform by using hummanta build --target=<target>.
If no target is specified, the default target from the hummanta.toml file will be used.
2. What should I do if the hummanta.toml file is missing?
If the hummanta.toml file is missing or hasn't been generated, you can run hummanta init to regenerate it.